|
|
SLEEKTM |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solid-Liquid Equilibrium Engineering KitLatest Release: Version 2.1SLEEK is CWB Tech's state-of-the-art software solution for crystallization process development. It shortens total development time, builds rapid understanding of the system, facilitates logical selection of solvents/experiments and reduce overall project cost. The development of crystallization-based separation processes is a complex multi-disciplinary problem. It requires a development team of process engineers and chemical scientists to collaborate on a multitude of tasks. These tasks can be classified under three headings: Experiments, Synthesis, and Modeling. Experimental tasks include laboratory work, collection of data, and expression of data into meaningful models. Synthesis tasks include understanding the underlying phenomena and system properties and creation of process alternatives. Modeling tasks include calculation and evaluation of these process alternatives. The development workflow is essentially an evolutionary approach among various experimental, synthesis, and modeling tasks. The goal is to generate feasible process alternatives and operating conditions and to evaluate their merits and potential. If you are involved in crystallization process development, you will know that this is very difficult due to the various types of complexities in the solid-liquid systems that you have to deal with. Time pressure, process regulations, and resource limitations also often hinder your development team in performing these tasks in the optimal manner. This is where SLEEK can add value to your development workflow. It provides efficient easy-to-use tools for the experimental, synthesis, and modeling tasks. With these tools your development team can make the development workflow more efficient through:
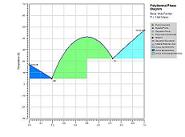
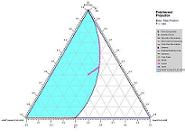
"SLEEK provides cutting-edge technology for the design of crystallization processes. We are confident that SLEEK will give us the boost we need to make our process development effort more efficient." Dr. Masashi Inaba SLEEK-for Thermodynamic AnalysisSLEEK has several features that will help you build comprehensive understanding of the solid-liquid system on hand. These features will help you to:
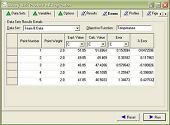
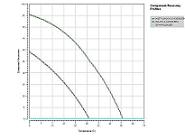
SLEEK-for Regression of Experimental DataOne of the most challenging development tasks is organizing experimental data and converting it into more meaningful and more useful form. With the help of binary and ternary (pseudo-binary) regression tools in SLEEK, you can:
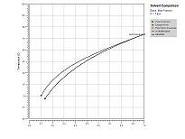
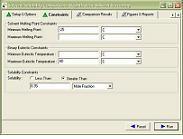
SLEEK-for Solvent SelectionSolvent and/or anti-solvent selection is very crucial for solid-liquid separation. SLEEK recognizes this importance and offers the following two tools to help you accomplish this task:
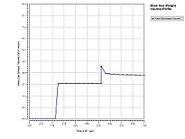
SLEEK-for Continuous Crystallizer DesignWith the help of the SLEEK continuous crystallizer design tool, you can calculate the percent recoveries, total heat requirement, and crystallizer performance under specified operating conditions. This design tool has models that allow you to calculate the particle size distributions by taking into account the effects of crystallizer size, nucleation and growth, agitator speed, fines dissolution, and product classification. SLEEK also has a powerful sensitivity analysis tool that lets you study the effects of design variables on the performance of your crystallizer. These tools enable you to:
SLEEK-for Batch Crystallizer DesignSLEEK batch crystallizer model allows you to create your own batch operating policies and then study the effect of these policies on crystallizer performance. The batch crystallizer model also lets you calculate the particle size distribution properties dynamically. With these capabilities you can do the following:
SLEEK comes with an intuitive and user-friendly architecture and interface, so you can learn to use it in a short time. At its core is a powerful engine that is based on proven technologies. It has a built-in pure component database with over 1500 components and a built-in aqueous component database with over 1000 components, so you don’t have to search for physical property information and can get off to a quick start. It also provides a local database, so you can store new physical properties and thermodynamic model parameters and share them with other users. Whether you want first to try a quick simulation to get an idea of what experiments to perform, or you would rather go to the lab to measure the phase diagram before doing the design calculations, SLEEK can handle the right amount of data at the right time. How to OrderTo place an order, or for more information, please contact us by phone, or by email at sales(at)cwbtech.com. Reference Publications
If you would like to request a copy of any of the above papers, please click here.
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||